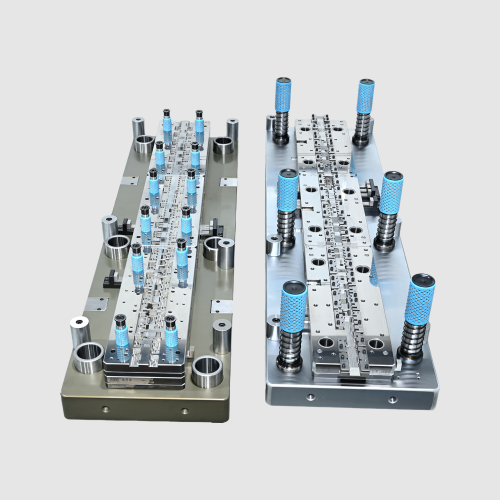
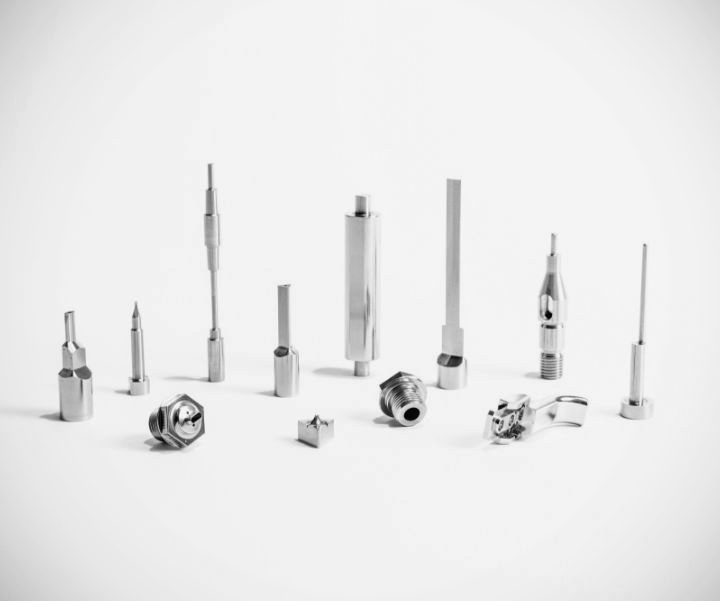
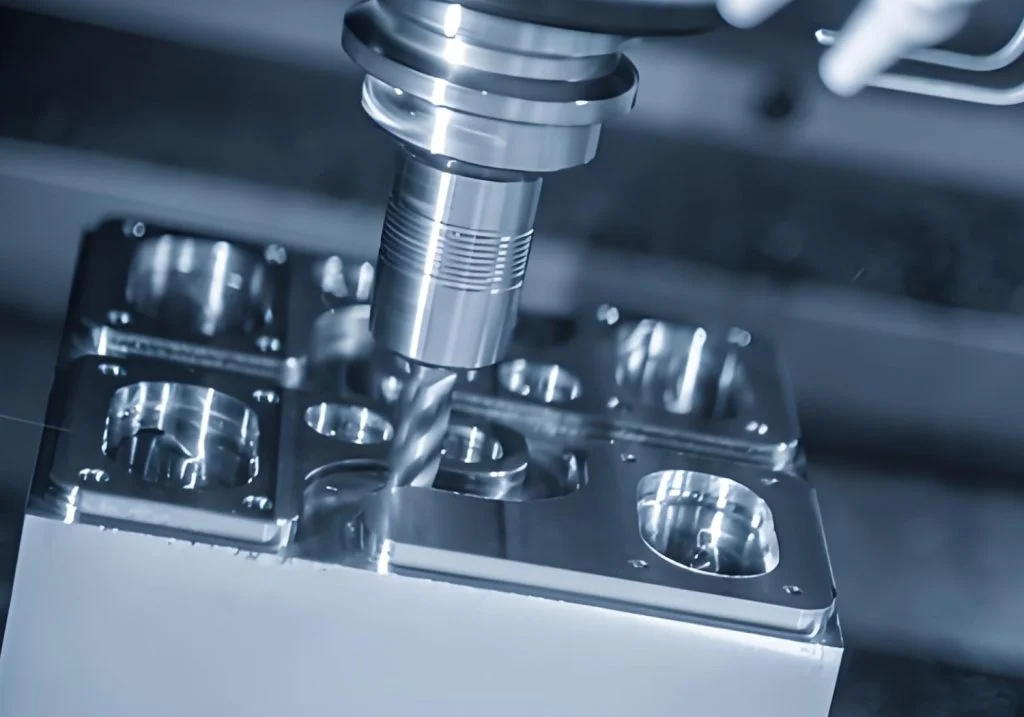
Precision machining and CNC machining are two distinct processes, both commonly used in the manufacturing industry, but serving different purposes. Many people confuse the distinction, so we’ll explain the differences below to help you choose the most appropriate process for your project.
Defining CNC Machining
CNC machining refers to the use of Computer Numerical Control systems to guide machine tools. The process automates cutting, milling, drilling, or turning by programming instructions into the equipment. CNC machines reduce human error and improve production efficiency. Their primary strength lies in repeatability and speed, particularly for large-scale production runs.
Defining Precision Machining
Precision Manufacturing involves producing components with extremely tight tolerances and high accuracy. It does not necessarily mean automation, though CNC is often part of it. The key goal is to achieve exact measurements, smooth finishes, and flawless parts. For example, when creating precision dies used in stamping connectors or Type-C interfaces, manufacturers must maintain tolerances within microns. Industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and electronics depend on Precision Manufacturing to meet strict performance standards.
Core Difference Between CNC and Precision
The primary difference lies in scope and focus. CNC machining is a method of using programmed machines. Precision machining is a goal—the pursuit of exactness and fine detail. While CNC machines can perform precision machining, not all CNC work requires the same level of precision. Similarly, precision machining can be accomplished with CNC or manual methods, as long as the required tolerances are met. In die-making, CNC equipment can cut base shapes, but precision machining ensures the punches and dies align perfectly for repeatable stamping.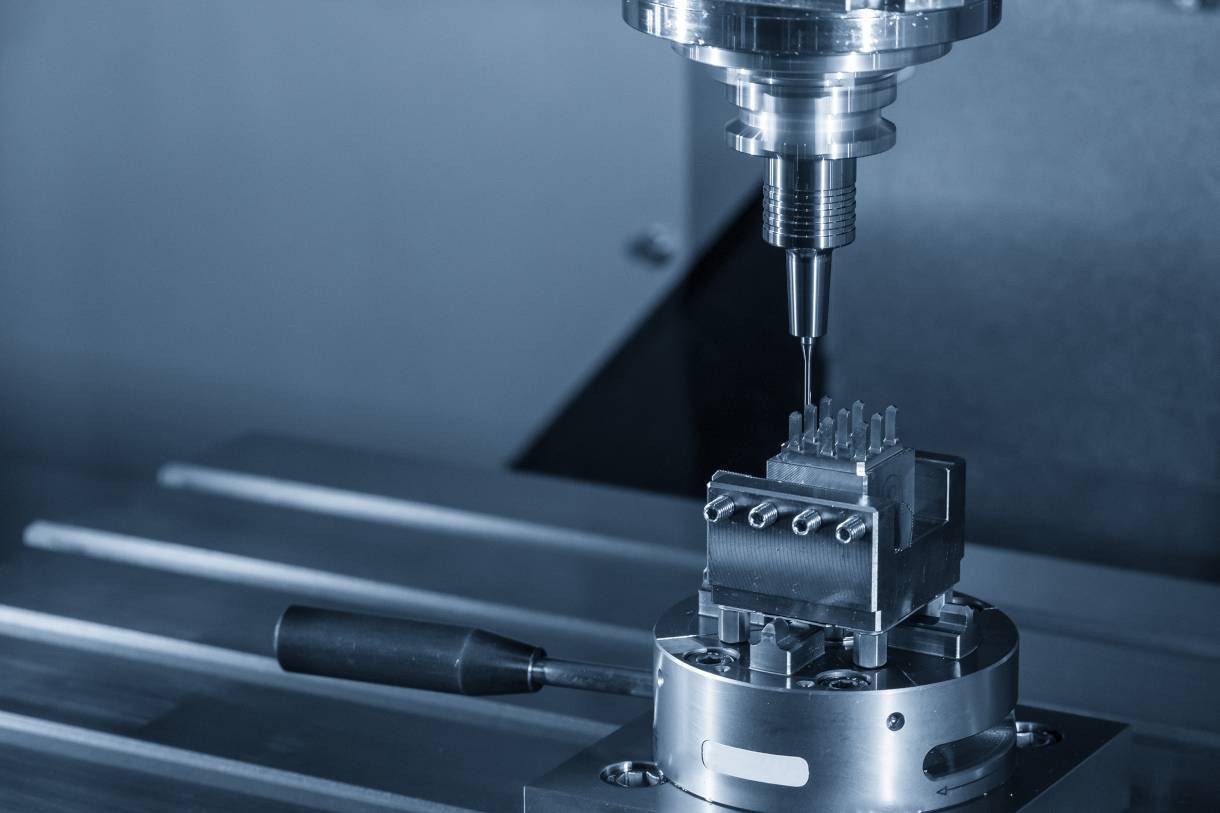
Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining is widely used in industries where consistent production matters. Automotive parts, consumer electronics, and general machinery benefit from the speed and efficiency of CNC machining. It is the go-to process for creating thousands of identical components. For example, CNC milling machines are used to rough-cut large die plates before the finer finishing is handled with Precision Manufacturing. CNC machining shines when accuracy is essential, but not at the highest tolerance levels required in advanced industries.
Applications of Precision Machining
Precision Manufacturing is essential for industries that cannot afford to fail. For example, medical implants must fit the human body perfectly. Aircraft engine parts must withstand extreme conditions with no error. Even minor deviations could cause safety risks. In tooling industries, precision dies used for stamping high-frequency connectors or thin metal sheets require flawless surfaces and ultra-tight tolerances. This makes precision machining indispensable in high-tech and safety-critical fields.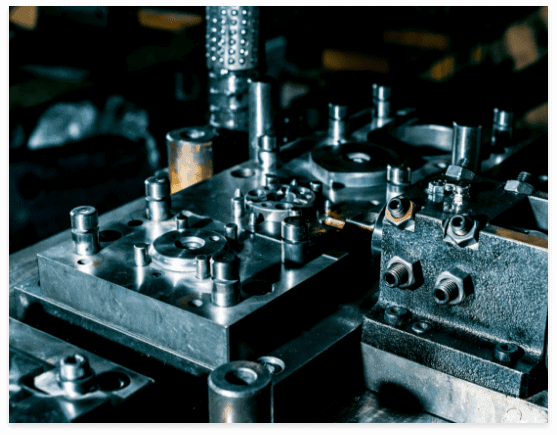
Technology and Equipment Used
CNC machining relies on programmed commands and versatile machine tools such as mills, lathes, or routers. Precision machining, which often utilises CNC equipment, also encompasses techniques such as grinding, electrical discharge machining, and micro-machining. For instance, wire EDM is commonly used in manufacturing precision dies, ensuring sharp corners and smooth profiles that stamping tools demand. These methods allow for extremely tight tolerances and surface finishes that standard CNC cutting cannot consistently achieve. Both approaches benefit from modern software and advanced tooling.
Cost and Efficiency Considerations
CNC machining is generally more cost-effective for mass production. Once programmed, machines can run continuously with minimal oversight. Precision machining, however, often incurs higher costs due to the use of specialised tools, extended setup times, and rigorous quality checks. The trade-off is superior performance and durability of the finished product. A good example is in die-making: CNC can quickly create the overall form, but precision machining ensures the final die can withstand millions of stamping cycles without failure. Businesses must balance budget, volume, and required tolerances when choosing between the two.

Choosing Between CNC and Precision Machining
The difference between CNC machining and Precision Manufacturing comes down to process versus purpose. CNC machining emphasises automation and repeatability, making it an ideal choice for standard production. Precision Manufacturing emphasises accuracy and reliability, serving industries where safety and function are critical. In many cases, companies combine both approaches. CNC machines deliver efficiency, while precision machining ensures perfection. Whether it’s producing complex aerospace parts or manufacturing precision dies for thin sheet stamping, understanding when to apply each process helps businesses optimise performance, cost, and quality. Industries that require the highest standards will always depend on precision machining.




