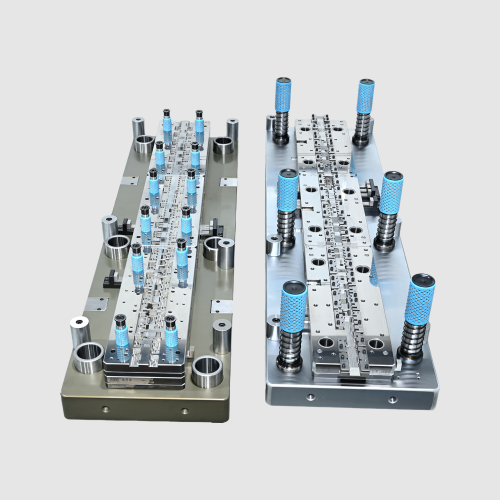
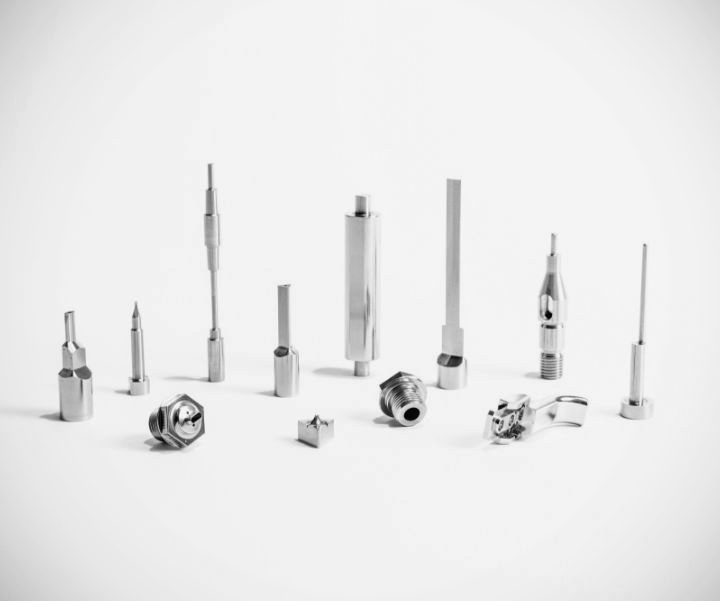
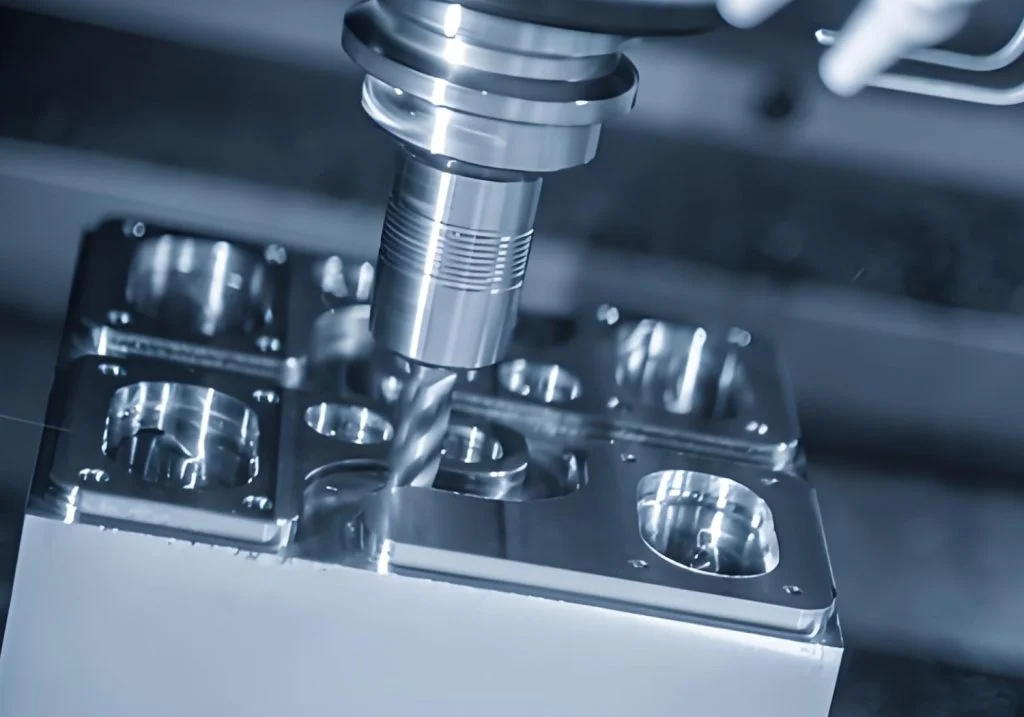
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies refer to precision tools used to cut, form, or shape sheet metal into specific parts. These dies are crucial for the mass production of products in the automotive, aerospace, electronics, and appliance industries. They ensure each component meets tight tolerances, repeatability, and quality standards required for high-volume manufacturing.
Types of Metal Stamping Die
Manufacturers use several common types of metal stamping dies, each serving a specific purpose. Blanking dies produce simple shapes by cutting through the material. Piercing dies punch holes. Bending dies shape parts along straight lines. Deep drawing dies are used to form complex cylindrical or box-shaped pieces. Progressive dies enable multiple steps to be completed in a single operation.
These types illustrate the flexibility of Sheet Metal Stamping Dies. They range from simple single-action fixtures to multi-stage progressive setups. Precision sheet metal tools must align, clamp, and cut with extreme accuracy. This ensures minimal material waste, tight tolerances, and high throughput efficiency in large-scale production runs.
Materials and Design Considerations
Choosing the right material and design for a Sheet Metal Stamping Die depends on the volume, metal type, and part complexity. Common die materials include tool steels such as D2, A2, or H13. These steels offer a combination of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance. For extremely high volumes, carbide inserts may be added for durability.
The design also considers blank clearance, punch radius, and part thickness. Precision sheet metal tools require careful calculation of clearance to avoid poor cuts or premature wear. Designers also integrate proper die seats, guide rails, and sensors to ensure smooth die operation and long lifespan.
Precision Sheet Metal Tools and Tolerances
Precision is the hallmark of a good Sheet Metal Stamping Die. Tolerances often fall within ±0.05 mm, depending on the part and industry standards. Achieving this level requires meticulous tool grinding, heat treatment, and assembly. Toolmakers frequently use CNC machining, EDM, and die-sinking for mold preparation.
Furthermore, progressive dies often include in-die gauging probes. These probes monitor form quality and part alignment during the stamping process. They ensure each part matches specifications. This constant quality check helps manufacturers meet tight tolerances with metal stamping dies.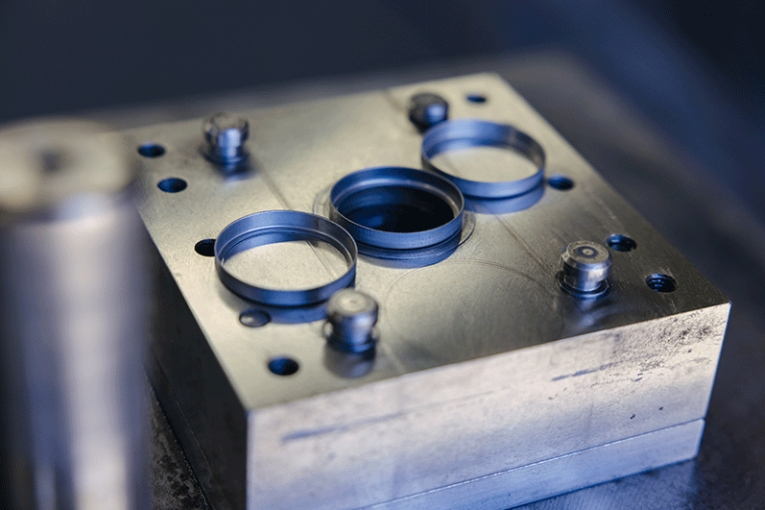
The Production Process Step by Step
In a typical stamping process, a sheet coil is loaded into a press equipped with a Sheet Metal Stamping Die. The press cycle pushes the punch into the die, cutting or forming the metal. In progressive dies, multiple forming stages occur within a single operation, utilizing sequential tooling elements.
Afterward, the die ejects the formed parts and automatically removes the scrap strips. Precision sheet metal tools ensure consistent alignment between stages. This enables reliable and repeatable production runs. As a result, flows remain smooth, and downtime stays low.
Application Areas of Sheet Metal Stamping Dies
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies enable the mass manufacturing of various parts. In the automotive sector, manufacturers use them to produce body panels, brackets, and structural components. In electronics, they shape chassis, housing, and connectors. Appliances, HVAC systems, and lab equipment also benefit from precision sheet metal tools in stamping applications.
Manufacturers choose stamped parts because they’re cost-efficient at scale and offer high precision. Tooling costs are amortized over large runs. This makes stamping economically viable for medium to high volumes. Consequently, Sheet Metal Stamping Dies drive modern industrial manufacturing.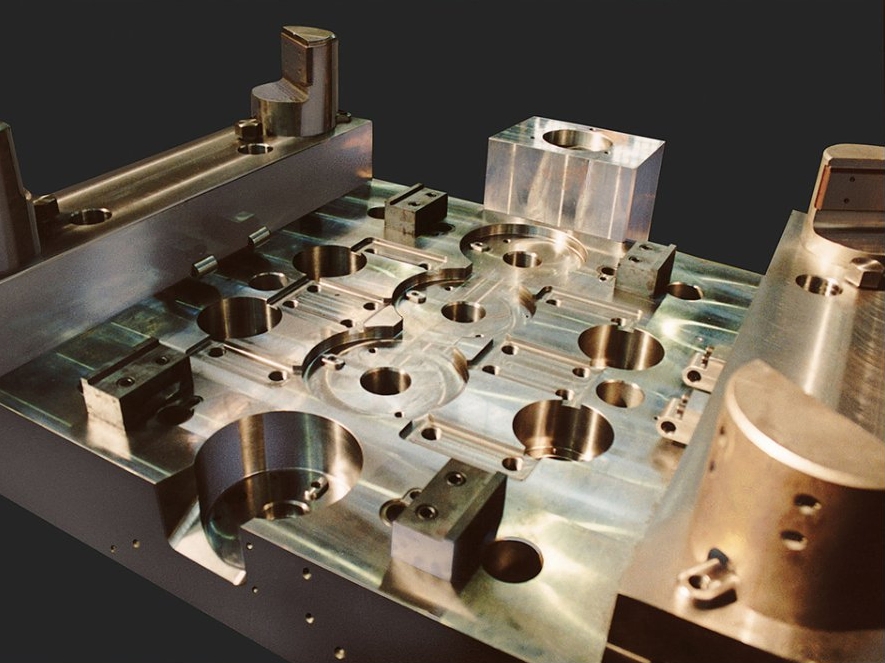
Maintenance and Tool Life Strategies
Keeping Sheet Metal Stamping Dies in peak condition requires regular maintenance. Toolmakers inspect for wear, burrs, and misalignment. Preventive grinding, polishing, and cleaning maintain part quality. For progressive dies, die blocks and rails are frequently lubricated and calibrated.
By replacing worn components early, manufacturers preserve precision and reduce unplanned downtime. Precision sheet metal tools should undergo scheduled die recertification to ensure optimal performance. This ensures consistent output over long production runs and maintains quality standards.
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies in Mass Production
Sheet metal stamping dies play a central role in the mass production of high-precision metal parts. These precision sheet metal tools enable fast, repeatable, and cost-effective manufacturing across various industries, including automotive, electronics, and appliances.




