Stamping dies are the backbone of the metal forming industries. By 2025, the global manufacturing sector is expected to face higher efficiency demands, shorter product cycles, and increasingly stringent sustainability regulations. Companies in automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics must rethink their die strategies. This article outlines market trends, data-driven insights, and how manufacturers adapt to evolving conditions.
Automotive Electrification Driving Die Demand
Electric vehicles reshape tooling requirements. EV battery housings, connectors, and lightweight structures require advanced stamping dies. According to MarketsandMarkets, the global EV market will reach $906 billion by 2028, growing at a 22% CAGR. This expansion increases demand for dies capable of handling aluminium and high-strength steels. Automakers like Tesla and BYD already push suppliers to deliver dies with higher durability and accuracy. These requirements are transforming the design and deployment of stamping dies.
Lightweight Materials and Design Innovation
Manufacturers adopt lightweight alloys to improve fuel efficiency and meet CO₂ targets. Stamping dies must now be able to handle aluminium, magnesium, and advanced high-strength steels (AHSS). However, these materials increase tool wear and require specialised coatings. According to the International Energy Agency, 70% of automakers plan to integrate more lightweight alloys by 2025. Die makers respond with optimised heat treatments and hybrid die concepts to extend tool life. The shift in material preferences directly influences the design of stamping dies.
Automation and Digital Twins
Automation reduces setup time and boosts throughput. Many factories now use digital twins to simulate die performance before cutting steel. Deloitte reports that 75% of manufacturers with digital twin adoption saw a 20% reduction in downtime (link). In stamping die applications, this means faster validation and fewer trial runs. Robotic integration further improves press efficiency, while predictive maintenance software extends die life. These innovative manufacturing practices are now essential for producing stamping dies.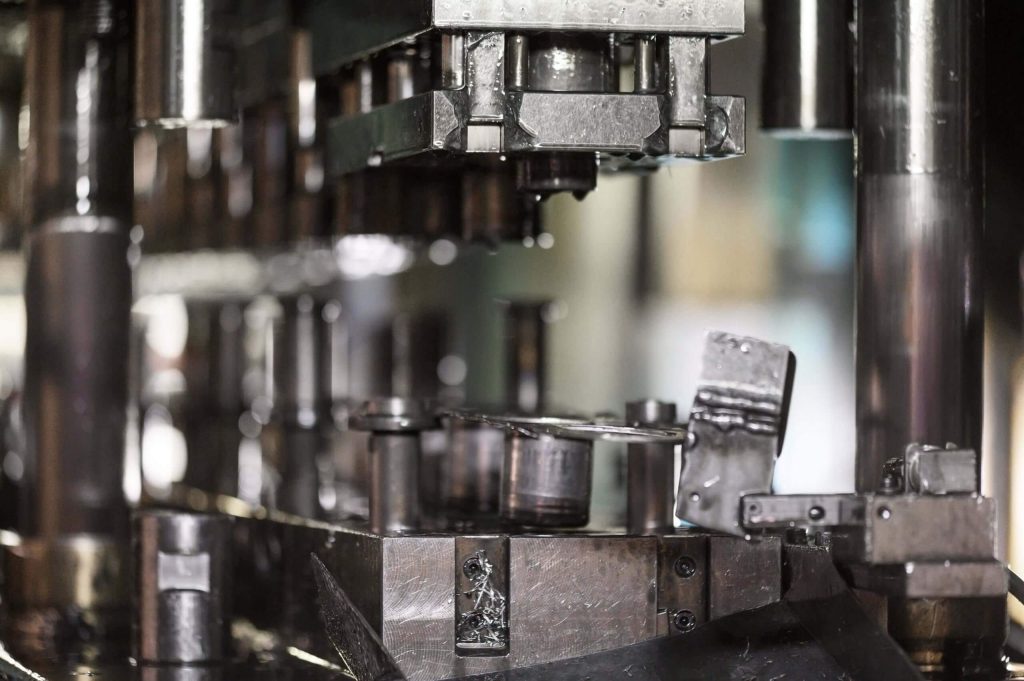
Regional Shifts and Supply Chain Adjustments
The stamping die market is shifting geographically. The Asia-Pacific region leads production, but reshoring trends in the U.S. and Europe are altering global supply chains. According to Grand View Research, the Asia-Pacific region held 45% of the die demand in 2023; however, North American growth is accelerating due to reshoring policies. Manufacturers respond by building local die facilities closer to OEMs. This reduces logistics costs, supports faster iterations, and stabilises supply chains. The regional transition puts new pressures on stamping dies.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations are now major drivers in the manufacturing sector. Energy-efficient stamping processes cut costs and align with corporate ESG goals. For example, Schuler Group reports that servo presses reduce energy use by up to 30% compared to mechanical presses. Additionally, coating technologies reduce the need for lubrication, thereby lowering the environmental impact. As OEMs adopt stricter sustainability metrics, stamping dies must adapt to more environmentally friendly production methods.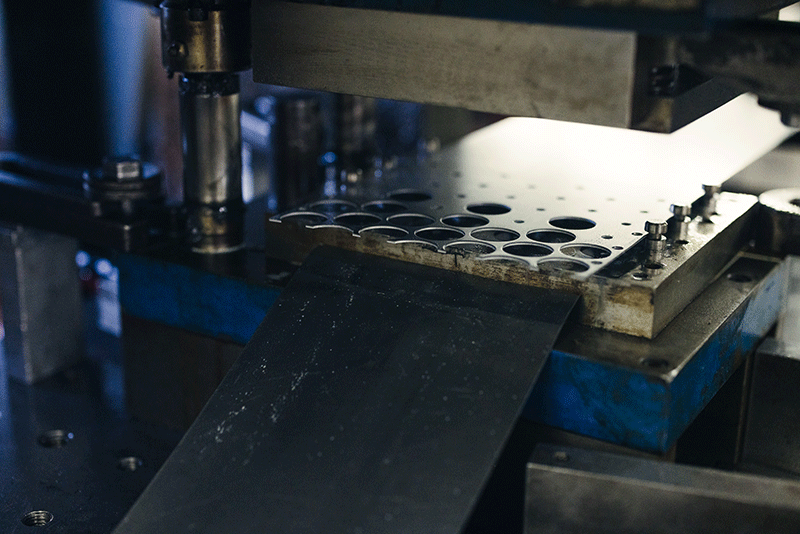
Customisation and Shorter Product Cycles
Consumer demand for faster product updates forces manufacturers to shorten die development cycles. In the consumer electronics industry, new smartphone and laptop models are launched annually. This requires stamping dies to be flexible and quickly retooled. PwC’s survey shows that 60% of manufacturers prioritise agile tooling capabilities to remain competitive. Modular die designs and precision inserts allow faster changeovers. This level of flexibility ensures stamping dies stay relevant in fast-paced markets.
Investment in Skilled Workforce
As automation advances, skilled engineers remain vital for the innovation of stamping dies. Toolmakers must combine traditional craftsmanship with digital tools to achieve optimal results. The U.S. Bureau of Labour Statistics notes a 3% annual increase in demand for tool and die makers through 2032. Companies invest in training to close skills gaps, especially in CNC machining, CAD/CAM, and heat treatment expertise. This human factor remains a core strength in stamping dies development.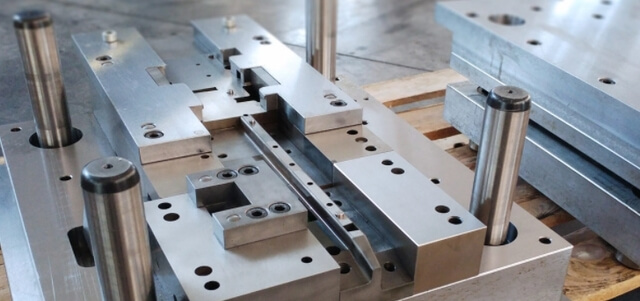
Stamping Dies Market Trends 2025
By 2025, the stamping die will be shaped by electrification, lightweight materials, digital tools, and sustainability. Verified data shows rising demand for durable, flexible, and eco-efficient dies. Manufacturers who adapt through automation, local production, and workforce investment will thrive. The future belongs to those aligning the technology with market forces. Ultimately, stamping dies remain at the heart of industrial progress.




