Choosing the right precision die-cutting equipment starts with evaluating your production requirements. Consider the types of materials you handle, their thickness, and the complexity of the parts you work with. For example, cutting foam gaskets or rubber sheets differs significantly from cutting thin metal sheets. Production volume also plays a critical role. High-speed rotary presses or automated systems are suitable for mass production, while smaller hydraulic or mechanical presses work better for prototyping or low-volume runs. Assessing your workflow ensures that your investment matches operational goals and prevents overcapacity or inefficiencies. Understanding these requirements also helps in forecasting future upgrades if product lines expand.
Evaluating Machine Types and Capabilities
Various types of die-cutting machines offer different capabilities. Mechanical presses provide consistent force and speed, making them ideal for repetitive operations on rigid materials. Hydraulic presses allow adjustable pressure, which protects delicate or layered materials from deformation. Rotary die cutting machines excel in the continuous production of flexible materials, including labels, films, and composite sheets. Modern laser-assisted and CNC-controlled die cutters can produce intricate patterns with minimal setup time. Some advanced systems also integrate software for real-time monitoring of cutting quality. Understanding these capabilities enables manufacturers to select machines that align with the complexity of the parts, the types of materials used, and their production goals.

Assessing Cutting Accuracy and Tolerance
Precision die cutting is only as good as its accuracy. Examine tolerance specifications and repeatability before selecting equipment. Standard packaging applications may allow tolerances around ±0.05 mm. In contrast, electronics, medical, or aerospace components often require tighter tolerances, sometimes as tight as ±0.01 mm. Machines that support micro-adjustments and provide consistent repeatability minimize scrap rates and reduce post-processing requirements. Consider features such as precision alignment systems, digital readouts, or automated feedback mechanisms, which ensure high-quality output throughout long production runs. Maintaining consistent tolerances ensures finished products meet customer expectations and industry standards.
Considering Material Compatibility
Not all die-cutting machines are capable of handling every material efficiently. Metals, plastics, foams, rubber, laminates, and composites each have unique cutting characteristics. Ensure the equipment can accommodate the hardness, thickness, flexibility, and layer configurations of your target materials. Multi-tool or interchangeable tooling systems can allow quick swaps for different materials, saving time and reducing downtime. Additionally, some machines include pressure control, specialized blades, or cooling systems to handle heat-sensitive materials. Matching the equipment to your material requirements ensures clean cuts, reduces tool wear, and prevents production delays caused by material incompatibility.
Evaluating Automation and Integration
Automation enhances efficiency, repeatability, and safety in die cutting operations. Look for machines that support automated material feeding, part ejection, and stacking. CNC-controlled systems enable the direct translation of digital designs into cutting programs, thereby reducing setup times and operator errors. Integration with other manufacturing lines, such as stamping or lamination processes, can streamline workflow and reduce manual handling. Robotics and sensors further improve accuracy while maintaining high throughput. Fully automated die-cutting solutions not only cut labor costs but also enhance quality control and minimize operational risks.
Reviewing Maintenance Requirements and Support
Even high-quality die-cutting machines require proper maintenance to perform reliably. Investigate service intervals, availability of spare parts, and the responsiveness of technical support teams. Machines with modular components, self-diagnostic features, and easy access to critical parts simplify upkeep. Preventive maintenance programs reduce unplanned downtime and extend the equipment’s lifespan. Choosing a manufacturer with comprehensive after-sales support ensures quick troubleshooting, which helps maintain production schedules and protects your investment. A reliable maintenance plan is essential for high-volume, high-precision operations.
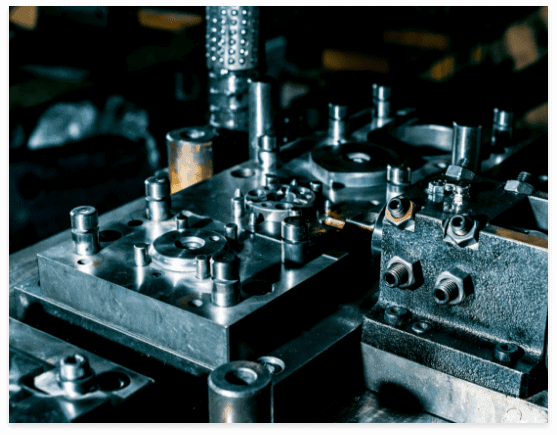
Budgeting and Total Cost of Ownership
The initial purchase price is only part of the investment. Consider energy consumption, tooling costs, consumables, and projected maintenance expenses. Equipment with higher upfront costs may offer longer tool life, better efficiency, or advanced automation features, resulting in lower total cost of ownership over time. Calculating operational costs over the machine’s lifespan provides a realistic financial picture of its expenses. This includes evaluating productivity gains, reduction in scrap, and potential downtime savings. A well-planned budget ensures the machine meets current production needs while remaining cost-effective in the long term.
How to Choose the Right Precision Die-Cutting Equipment
Selecting the right Precision die-cutting equipment requires balancing accuracy, material compatibility, automation, and cost. Test machines with real materials to validate performance under expected production conditions. Evaluate production speed, cutting precision, tool life, and ease of maintenance. Combining high-quality mechanical systems with advanced digital control ensures consistent product quality and operational efficiency. Investing time in a thorough evaluation yields reliable die-cutting solutions that minimize scrap, enhance output, and facilitate high-volume production.




