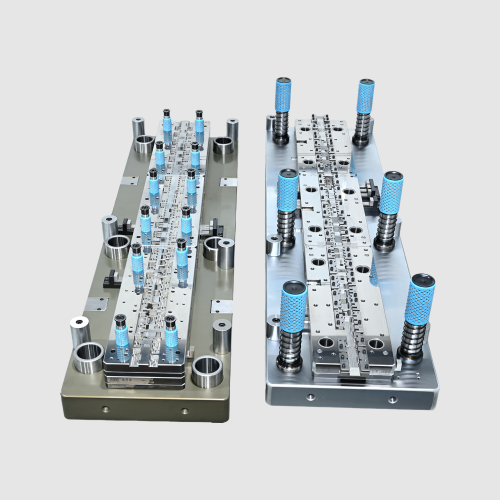
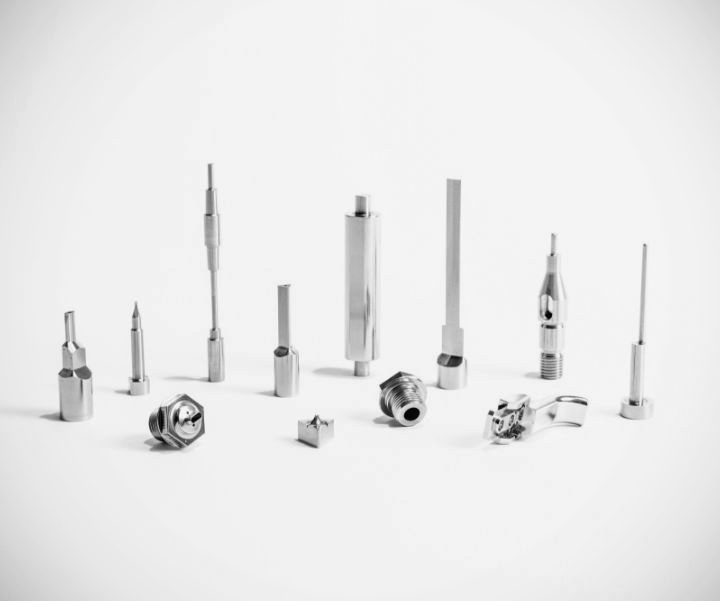
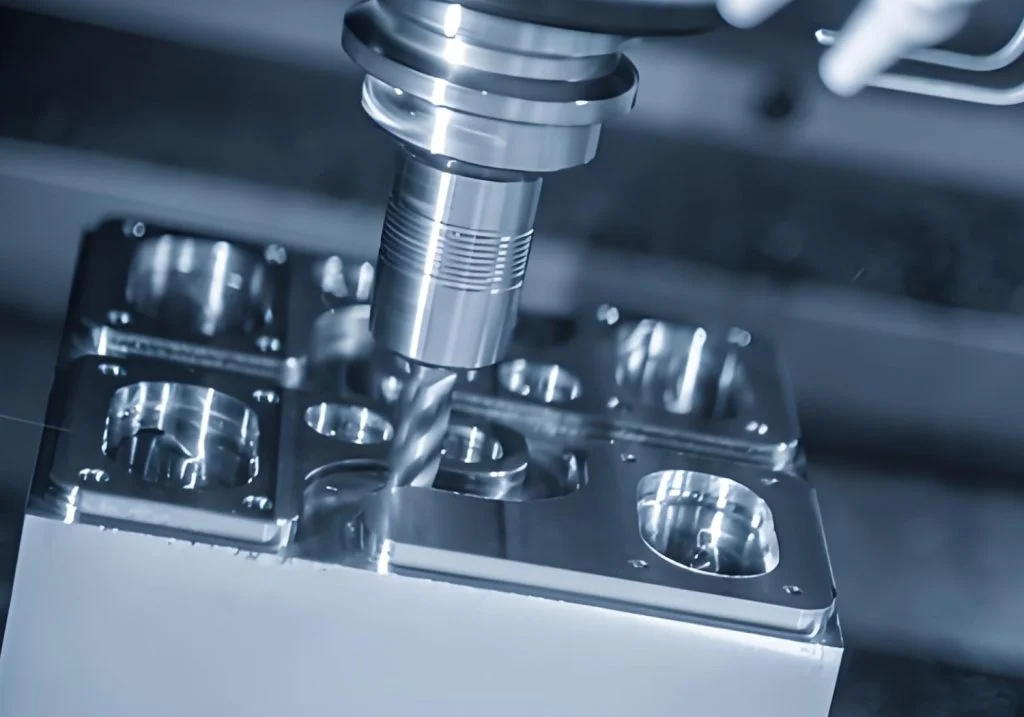
Precision machining plays a vital role in ensuring the dimensional accuracy and consistent performance of progressive stamping dies. In high-volume production environments, even the slightest deviation in die geometry can result in significant material waste or compromised product quality. By employing advanced machining techniques, manufacturers can meet tight tolerances, ensure part uniformity, and enhance the overall efficiency of the stamping process.
Understanding Progressive Stamping Dies and Their Tolerance Requirements
Progressive stamping dies comprise a series of workstations that shape the material in sequence as it passes through the die set. Each station performs a specific task—cutting, bending, coining, or drawing—until the final form is achieved. Given this chained workflow, any deviation at one station can compromise the entire output, which underscores the importance of exacting tolerances.
Tolerance in progressive stamping is not just a technical metric—it’s a critical factor in maintaining part interchangeability, operational safety, and compliance with industry standards. In many cases, tight tolerances of ±0.01mm or less are necessary, particularly when producing components for precision connectors or sensors. Precision machining is indispensable in achieving such demanding specs.
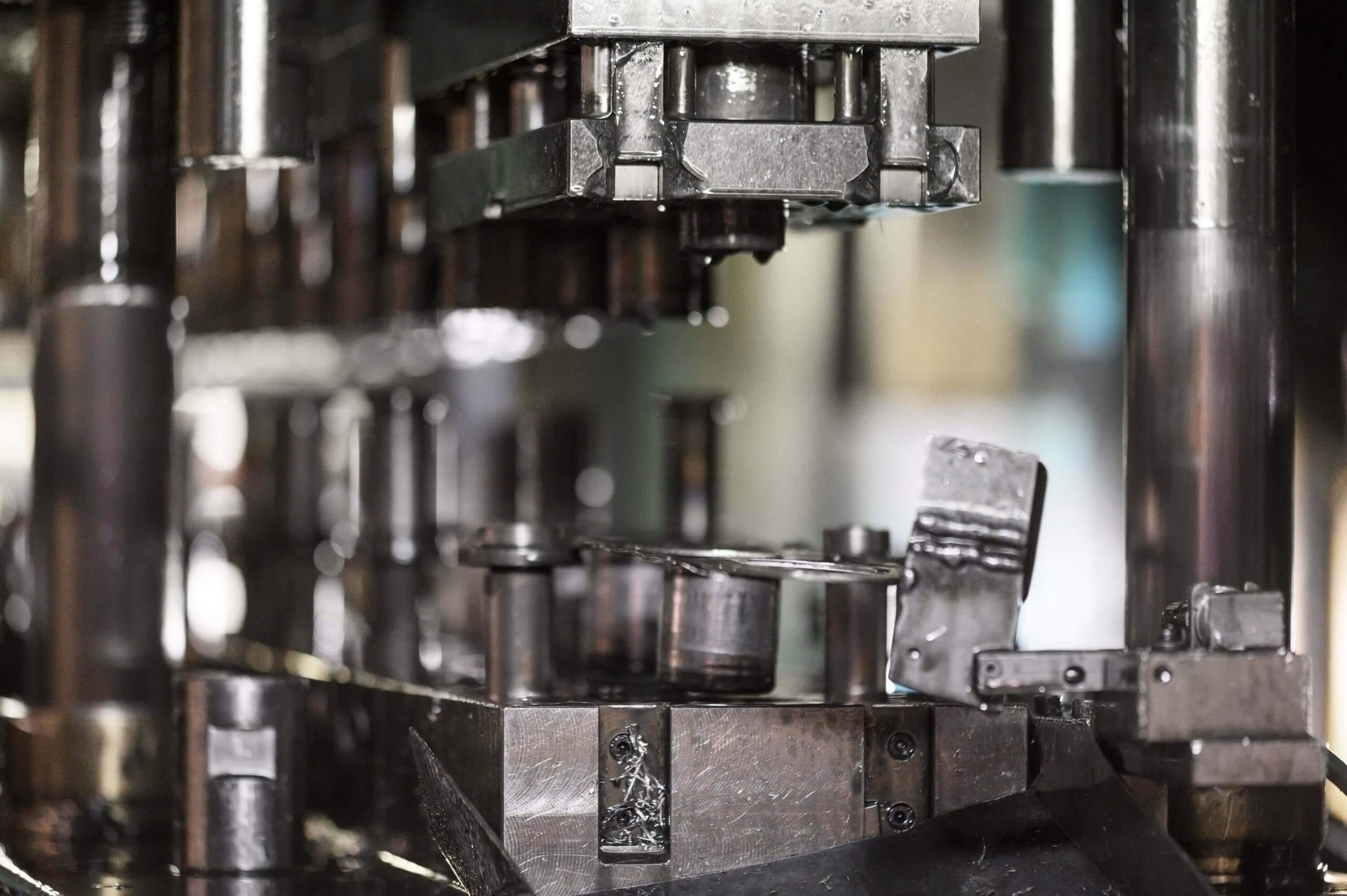

Critical Role of Material Selection and Design Geometry
While machining accuracy is essential, the effectiveness of progressive stamping dies also hinges on selecting suitable materials and designing geometries that align with performance requirements. High-speed steel, carbide, and powdered metals are often used for die components due to their hardness and wear resistance. However, machining these materials accurately requires specialised tooling and techniques.
Equally important is the design geometry of each die element—clearance angles, corner radii, and punch shapes must be tailored to both the workpiece material and the forming process. Precision machining enables engineers to execute intricate geometries with sharp detail, allowing for optimal material flow and reducing stress concentrations that could lead to premature die failure.
Precision Machining Techniques That Maximise Die Accuracy
A variety of machining techniques are employed to achieve the ultra-tight tolerances required in progressive stamping dies. These include wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), high-speed CNC milling, grinding, and jig boring. Each method is suited to specific geometries or materials, chosen based on the die’s shape, size, and intended function.
Wire EDM, for example, excels at producing intricate profiles and sharp corners without inducing mechanical stress. Meanwhile, CNC milling provides flexibility for multi-axis machining and can achieve mirror-like surface finishes when equipped with fine-tipped tools. Grinding and jig boring further refine surface precision and dimensional accuracy, especially for guide pins and bushings.
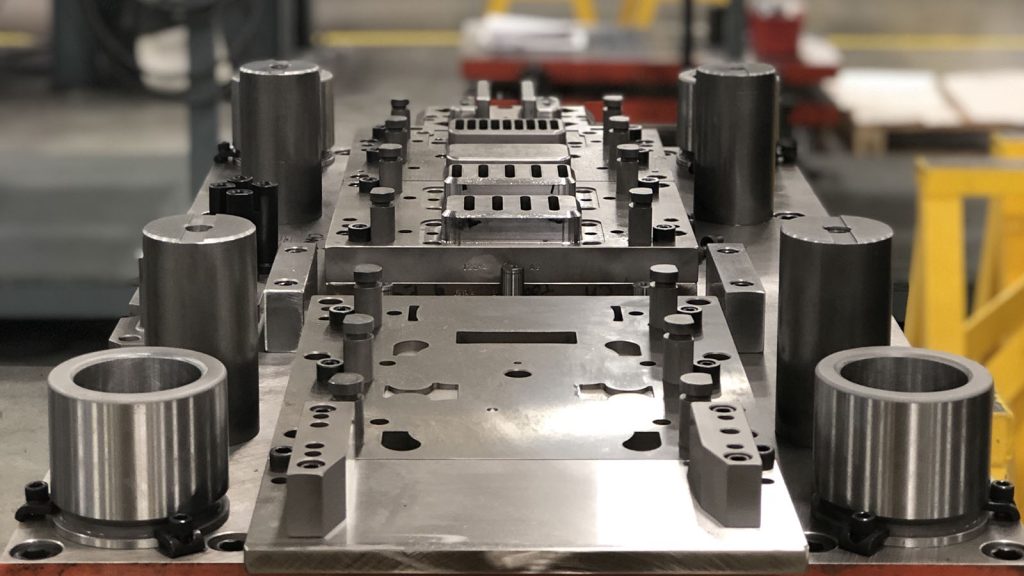

Minimising Wear and Deformation in High-Volume Production
Precision machining not only improves the initial accuracy of a stamping die but also directly contributes to its long-term durability. By ensuring smoother surfaces, tighter fits, and proper alignments, it reduces friction, heat buildup, and vibration during operation, all of which are key drivers of tool wear and deformation.
In progressive stamping operations that may involve millions of cycles, even a slight misalignment or burr can cause cumulative damage. Machined components with superior finishes and precise tolerance control help prevent these issues, thereby extending die life and minimising downtime. Surface treatments, such as polishing, nitriding, or coating, can also be applied post-machining to enhance performance further.
Impact of CNC Technology on Modern Stamping Die Fabrication
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining has revolutionised the design and manufacture of progressive stamping dies. The integration of CAD/CAM software enables engineers to simulate toolpaths, optimise cycle times, and verify tolerances before cutting commences. This digital workflow enhances accuracy while reducing lead times and human error.
Moreover, CNC systems offer unmatched repeatability and consistency across production batches. With closed-loop feedback systems and real-time monitoring, CNC machines can detect tool wear or positional drift and compensate automatically. This automation not only ensures higher accuracy but also frees skilled operators to focus on strategic tasks, such as process optimisation or developing custom tools.
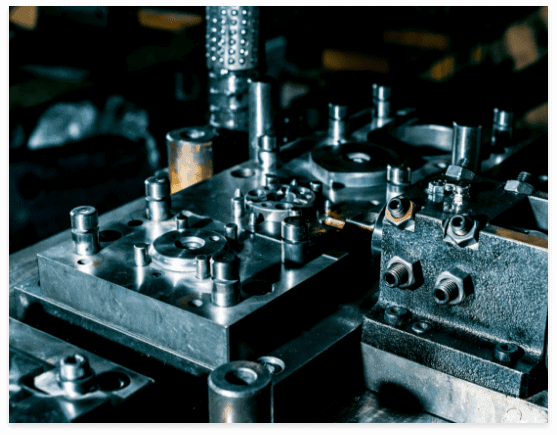
Quality Control Strategies that Leverage Precision Machining
Implementing rigorous quality control measures is crucial for ensuring that each die component meets its specifications. Precision machining complements these efforts by producing highly repeatable results, which simplifies inspection and reduces variability. Standard QC tools, such as CMMs, laser scanners, and comparators, rely on precision-machined surfaces for accurate measurements.
In some facilities, in-line metrology systems are integrated directly into CNC machining centres, allowing for immediate verification and correction of”tolerances. “This’ measure-while-machining’ approach reduces the need for downstream inspection and ensures defects are caught early. Moreover, precision machining enables traceability—each die component can be uniquely coded and measured with confidence.
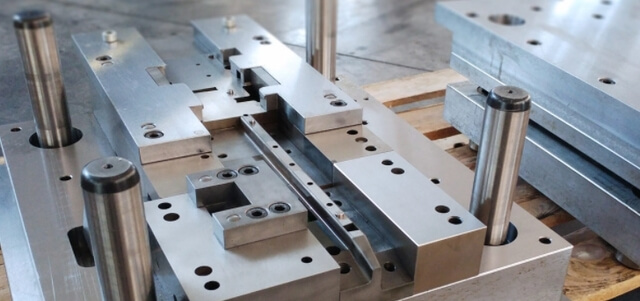
Integration with Automation and Tooling Innovations
Progressive stamping dies are increasingly integrated with automated feeding systems, sensors, and real-time monitoring tools. Precision machining ensures these complex systems work seamlessly together by enabling the tight alignments and reliable interfaces required for automation. For example, machined guide rails and locating pins help achieve exact strip positioning with minimal deviation.
Tooling innovations such as quick-change die sets, modular tooling blocks, and adaptive inserts also rely heavily on precision machining. These components must maintain dimensional accuracy even under high loads and frequent exchanges. As automation grows in stamping facilities, the demand for high-precision, easily replaceable die components continues to rise—driven by the machining methods that make them possible.
Sustaining Long-Term Accuracy through Precision Machining
Ultimately, the goal of precision machining in progressive stamping die manufacturing is not just to meet its design specs—it’s to sustain performance over time. Consistent accuracy is crucial for maintaining product quality, minimizing scrap, and preventing costly tool rebuilds. Through a combination of high-end equipment, skilled craftsmanship, and continual process refinement, manufacturers can extend tool longevity and lower the total cost of ownership.




