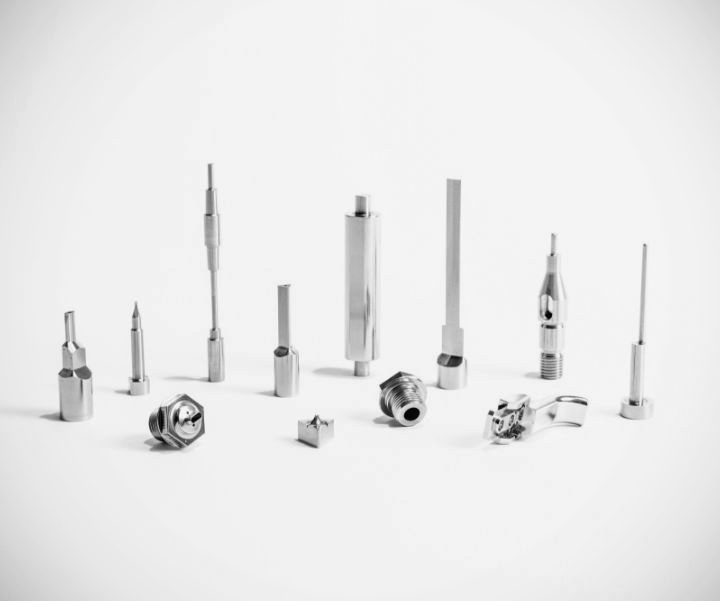
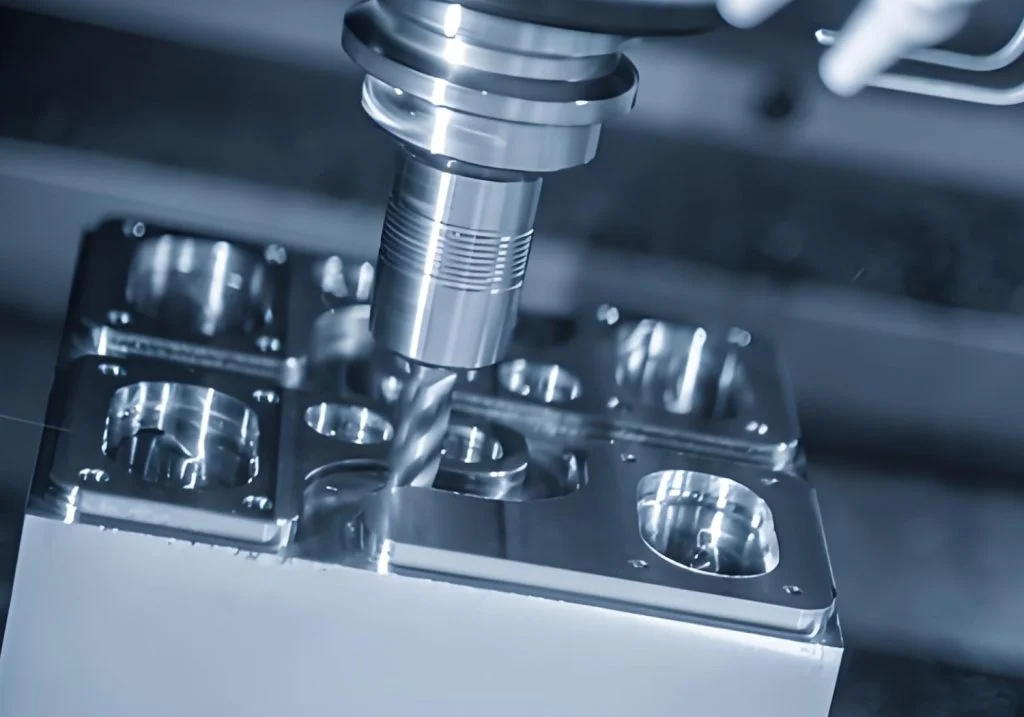
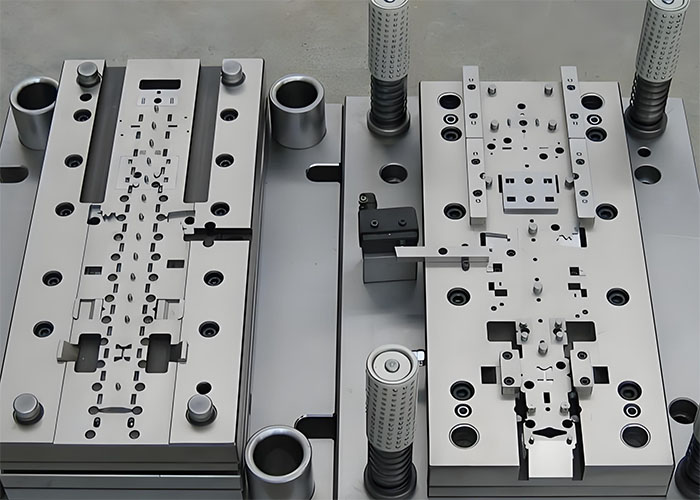
In the automotive manufacturing sector, stamping dies are the critical link between engineering design intent and high-volume production. A well-designed stamping die set not only cuts or forms metal but also ensures dimensional accuracy, repeatable assembly fit, and long-term process stability over hundreds of thousands of cycles. At Chaoyang, we treat stamping die sets design as a systems engineering problem: material selection, die base strategy, alignment accuracy, and adherence to industry standards (MISUMI, HASCO, DME) all impact cost, uptime, and part quality. We focus on tolerance control (down to ±0.01 mm), durable tool steels, and modular and customized die base solutions in our manufacturing processes.
Stamping Die Sets Design Principles
Design dictates manufacturability. For stamping die sets, we first translate functional part requirements into measurable die specifications. Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) symbols define critical dimensions, datum references, and tolerance ranges. Features that directly impact assembly fit, safety, and functional performance are prioritized; the tightest tolerances (e.g., ±0.01 mm) are reserved only for surfaces that truly require them. This reduces unnecessary costs and simplifies subsequent inspection.
Where possible, a modular die architecture is employed. Modular design separates standard components (die bases, guide posts, bushings) from custom inserts (blanking dies, drawing rings, forming inserts). This approach shortens lead times, reduces spare parts inventory, and allows you to reuse standard die bases across multiple components. For automotive projects that require frequent changes or have numerous derivative series, modular design provides flexibility and traceable repeatability. When necessary, we use progressive dies to deform the material in stages across multiple stations, distributing strain, reducing springback, and improving yield. We employ guiding features and positive locating to eliminate part float and maintain consistent strip indexing, which is critical for achieving repeatable dimensional control.
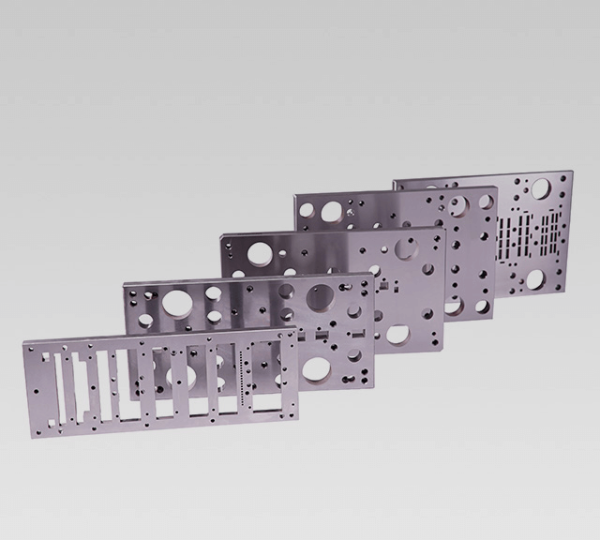
Materials, heat treatment, and durability strategies for stamping die sets
Durability begins with the right materials and heat treatment processes. For automotive stamping dies, we select tool steels and pre-hardened steels based on wear mechanisms and usage cycles. D2, A2, and H13, along with high-quality hot-work steels, are common choices: D2 offers excellent wear resistance in blanking operations; H13 provides good thermal shock resistance during hot forming or trimming; A2 combines toughness and formability, making it suitable for general-purpose molds.
In production, we utilize specific surface treatments and coatings to reduce adhesive wear and galling. Nitriding, PVD coatings, and cryogenic treatments can increase surface hardness and reduce friction. Additionally, pre-hardened steels provide a consistent baseline hardness without complex post-processing heat treatments, thus shortening lead times. For parts requiring final heat treatment, we allocate machining allowances and stabilization cycle times in the process control plan to compensate for deformation.
Standardization, Modularity, and Global Compatibility
Chaoyang-designed stamping die sets are compatible with widely adopted standards such as MISUMI, HASCO, and DME, while retaining the flexibility to produce fully customized die bases to meet specific needs.
Standardized die bases, guide pin dimensions, and bushing systems simplify maintenance across sites, reduce spare parts inventory, and accelerate supplier qualification. For multi-tiered, high-volume automotive production projects, adopting global standards reduces the risk of assembly mismatches and speeds up die replacement during service.
However, we continuously innovate in line with standards. We offer two product lines: one for standard die bases for rapid mass production, and another for customized production of complex parts or new model engineering projects with unique geometries or stamping clearances that require tailored solutions. It is crucial to ensure that the interface between custom inserts and standard die bases is well-documented to avoid integration errors.
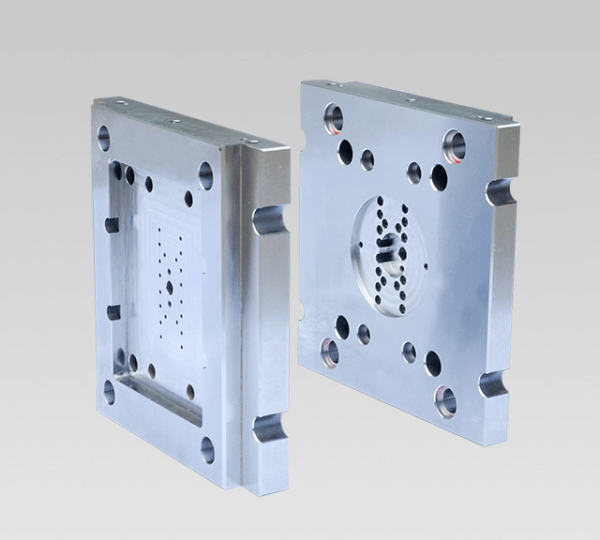

Precision Manufacturing, Tolerance Control to ±0.01 mm
Achieving tolerances of ±0.01 mm for automotivwithets requires rigorous manufacturing and inspection processes. Strict control of the machining process is paramount; therefore, we utilize high-precision CNC milling, EDM, and grinding to machine critical surfaces. We perform all machining in temperature-controlled areas and follow thermal stabilization procedures to minimize post-machining deformation. Additionally, when we set die clearances (the gap between the punch and the die, the shearing clearance), we consider thermal expansion, coating thickness, and wear during break-in. For example, blanking shear clearance varies depending on the material; the clearance range should be specified based on the material and thickness to maintain consistent burr and dimensional accuracy.
For critical cavities and stamping features that require micron-level shape accuracy, we recommend electrical discharge machining (EDM). Wire EDM and sinker EDM allow us to achieve consistent fillet radii and precise contours, and we can subsequently perform precision grinding and lapping to control surface finish and runout. For die components that use press fits, we maintain tolerances for shafts and holes to prevent the accumulation of minute displacements that could cause dimensional deviations in the stamped parts.
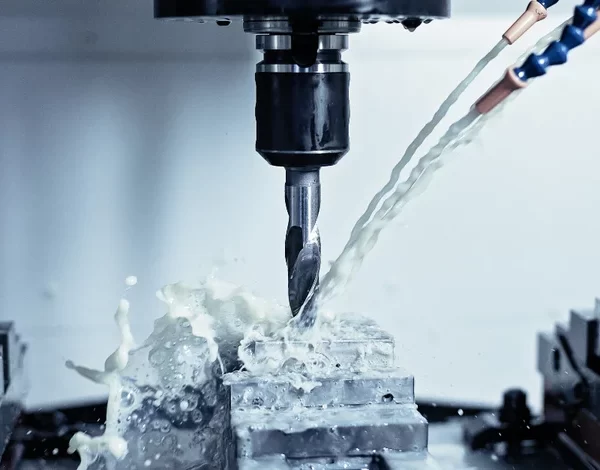

Application Areas and Process Integration
Manufacturers widely use automotive stamping dies to produce components such as body panels, chassis brackets, reinforcing rings, mounting flanges, and thin-walled structural parts. They also use these dies in areas outside the automotive industry, including electronic product housings, appliance chassis, consumer electronics, and specialized industrial parts. Each application has different technical requirements, ranging from ultra-thin thicknesses where springback is dominant, to thick-thickness drawing where blank holder force and strain hardening are critical factors.
When we transfer dies from the tool shop to the stamping shop, we ensure that the process documentation clearly and completely describes the strip layout, feed direction, material batch specifications, lubrication scheme, and recommended press settings. For progressive dies, we synchronize the station design with the strip feed and press dwell time. We set time margins for feeding, forming, trimming, and ejection to avoid collisions or misfeeds. For deep drawing or complex embossing processes, we use intermediate annealing and guiding chamfers to reduce localized thinning and extend die life.
Ensuring Precision, Durability, and Compliance
Chaoyang ensures the consistent quality and precision of stamping die sets by focusing on ±0.01 mm tolerance control, selecting durable tool steels and pre-hardened steels, and integrating modular or customized die base solutions. It also conforms to global standards such as MISUMI, HASCO, and DME, and, combined with rigorous process validation, preventive maintenance, and lifecycle management, ensures reliable performance in high-volume production environments.